For my new Blocksmurfer explorer I needed to investigate the block versions used in the history of Bitcoin to be able to analyse and parse those blocks. Every block on the Bitcoin Blockchain starts with a 4 byte version number, indicating which software is used to create the block and which BIPs (Bitcoin Improvement Proposals) it supports.
By looking at the block version we will get an overview of the main protocol changes in Bitcoin in the past.
To create the graphs Matplotlib is used, a local bitcoin node provided the blockchain and Bitcoinlib parsed the blocks. All blocks from the genesis block 0 to block 635000 from June 2020 are taken into account.
The first era - Block versions as integers
In the first 400000 blocks or so, the version bytes represented a simple integer. And in this first era 3 new protocol changes are adopted with the version numbers 2, 3 and 4.
As you can see in the graph below the first version change was a bit after block 200000 in the year 2012. The block version changed from version 1 to 2. The graphs show which percent of the blocks was using a specific version number per 1000 blocks.
This change was passed in a relatively short time and introduced BIP0034. In this protocol change the block height was added to the locking script (scripSig) of the coinbase transaction. By adding the height to the coinbase transaction duplicate transaction IDs are avoided and it also creates a way to extract block height from a block without other knowledge.
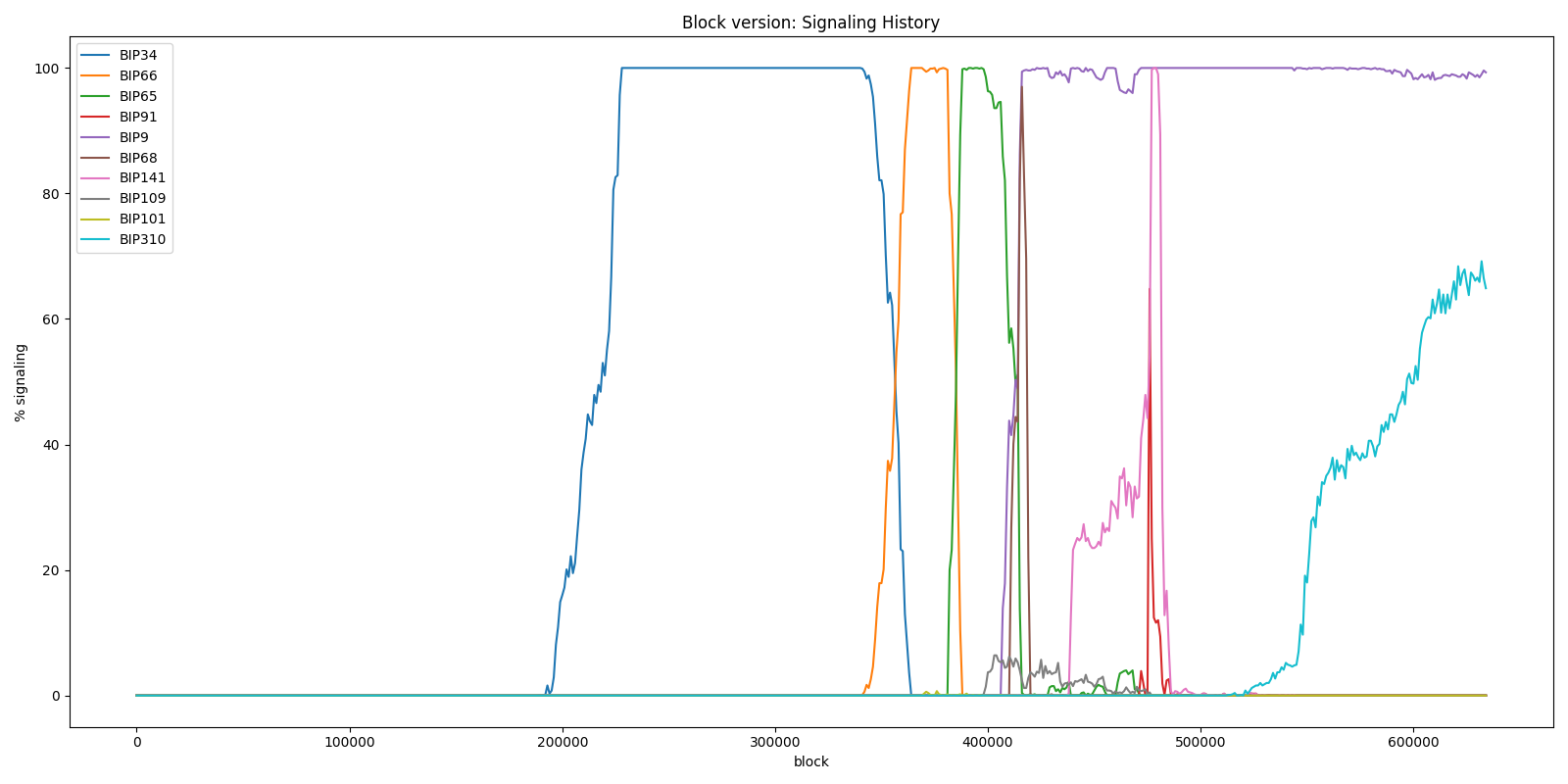
Then around block 370000 in 2015 BIP0066 was adopted. This protocol enforced strict DER encoding for signatures. Previously DER signatures which did not follow the standard would be marked as valid by a bitcoin node, causing problems if the underlying software (i.e. OpenSSL) of a bitcoin node changes.
Then shortly after this a new protocol change BIP0065 was accepted by the network. This allowed to create transactions which are only spendable after a certain date or block height using the CHECKLOCKTIMEVERIFY opcode.
The Second era - Introduction of a new versioning system
The integer based versioning system had as disadvantage that only one protocol change can be signaled at once. The versioning system described in proposal BIP0009 uses the 4 byte version as 32 individual bits. The first 3 bits are used to indicate which versioning system is used, currently '001' and the other 29 bits can be used to signal a specific protocol change.
So if you look at block 416000 for instance you see the block version in bytes is 0b00100000000000000000000000000001. So the versioning system is 001 and the last bit is set to 1 to signal a new protocol, BIP0068 in this case.
As you can see in the graph below BIP0009 was accepted shortly after block 415000 in 2016. And at the same time BIP0068 was accepted including the related BIP0112 and BIP0113. This was an important update allowing to create payment channels and paved the way for the lightning network. The sequence part of a transaction input is used as locktime, allowing to lock the input until a certain block or timestamp using the CHECKSEQUENCEVERIFY opcode.
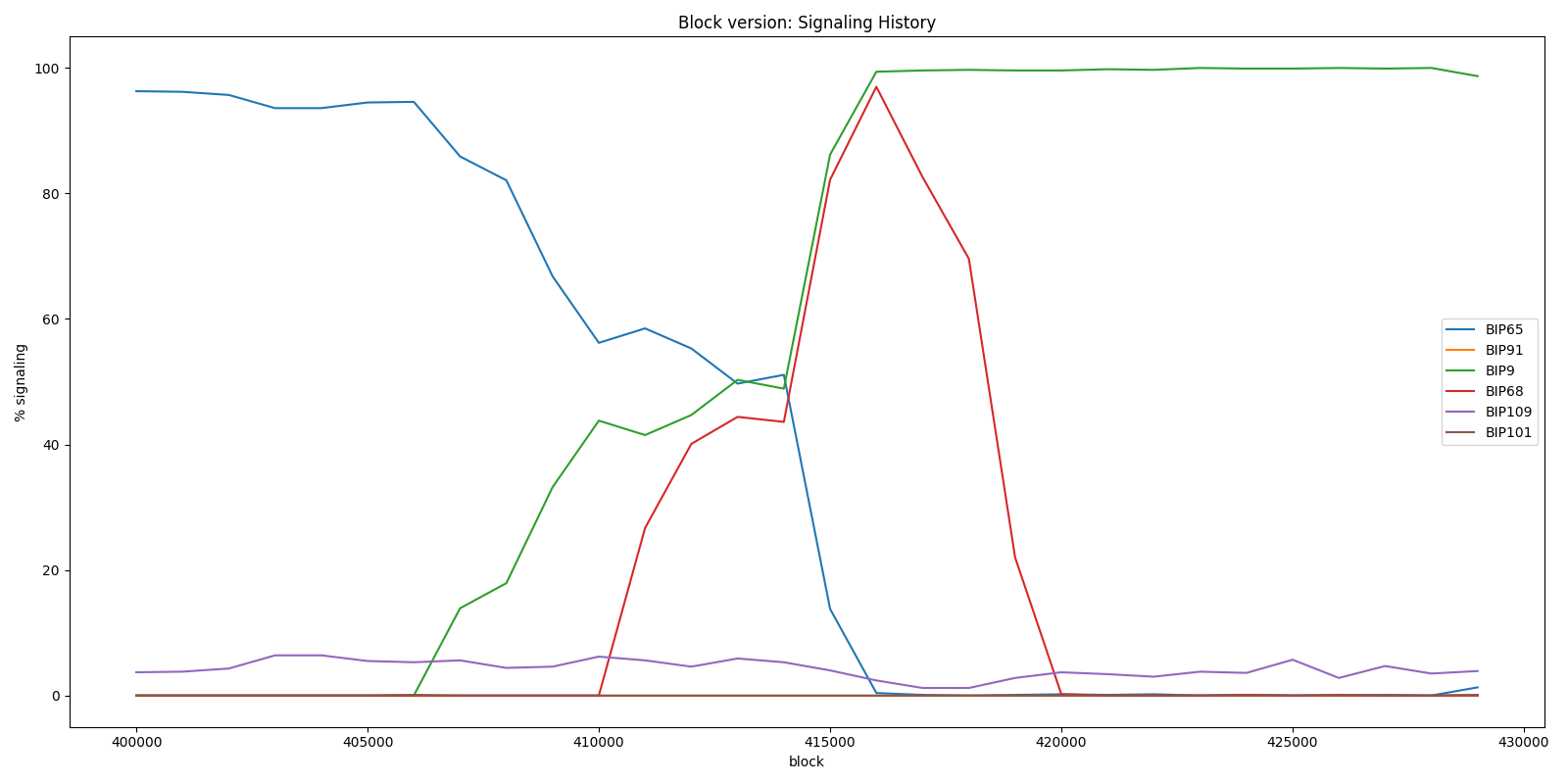
In the graph above, you also see the BIP0109 proposal in the 5% region, it was a more controversial proposal to increase to block size to 2Mb. It was never accepted but more proposals would follow starting a fierce debate.
The Third era - Block size, Segwit and the Bitcoin Civil war
At the end of 2015 Segregated Witness or Segwit was presented in BIP0141, BIP0143, BIP0147. With segwit the signatures (witnesses) are separated from the inputs. Segwit was one of the biggest changes to the bitcoin protocol so far, it fixed transaction malleability, increased block capacity, incentives to reduce the number of unspent outputs (utxo pool), reduces network traffic for SPV client and increased multisig safety among other benefits.
It took a long time and lot of discussions before Segwit got adopted as you can see below. For some reason the discussion got really political and a lot of virtual mud was slinging around. Some even called it Bitcoin civil war. The block size debate was roughly between people who oppose Segwit and wanted to increase the block size and people who want Segwit without block size increase.
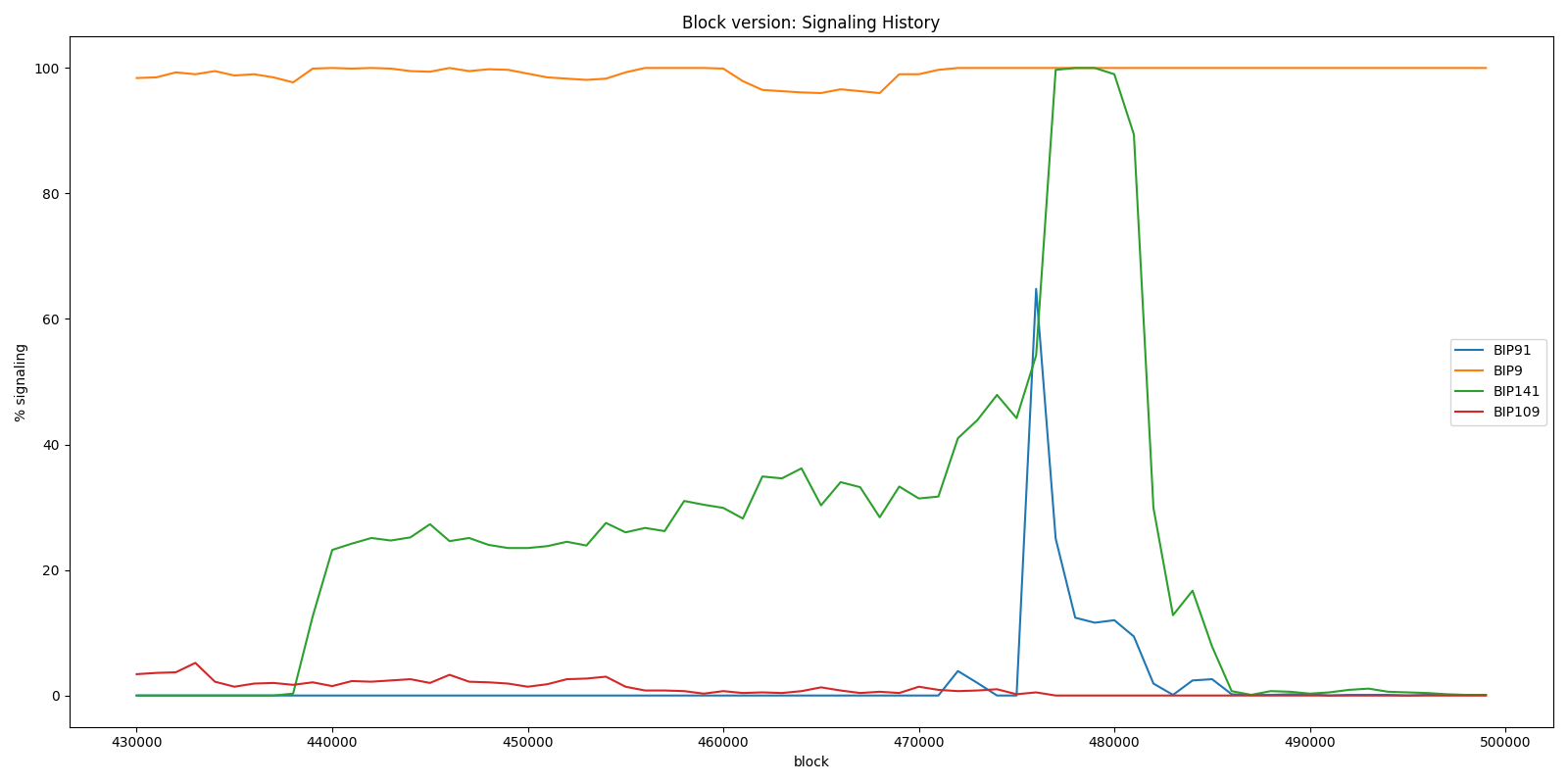
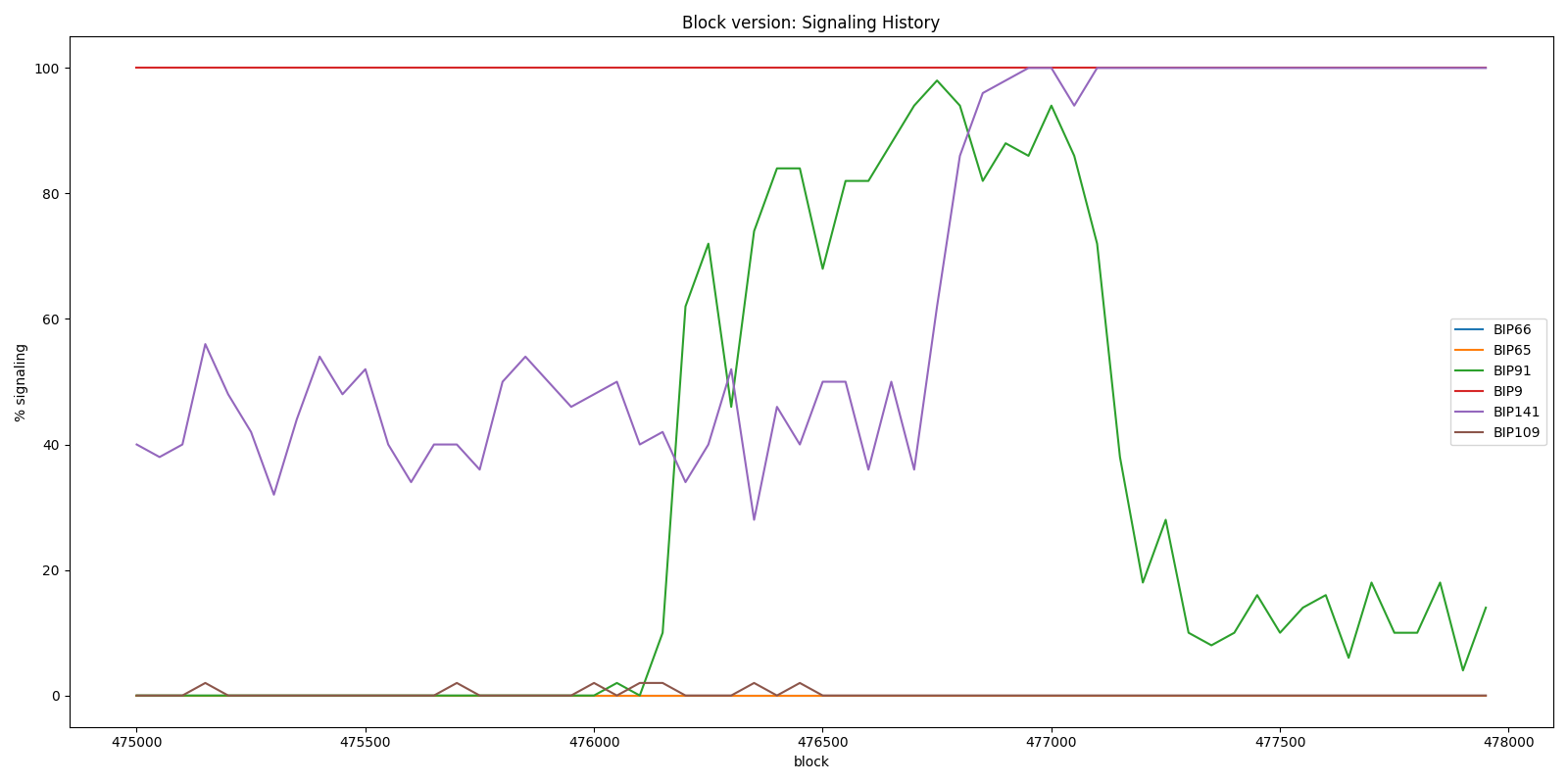
After a while as a compromise BIP0091 or Reduced threshold Segwit MASF was created in which miners and Bitcoin companies declared to activate Segwit and increase the block size to 2Mb. As you can see in the graph below Segwit was activated shortly BIP91 was accepted. The hard-fork block size increase was never adopted.
Recent History
After Segwit no changes to the Bitcoin protocol have been introduced. You can see BIP0310 in the top graph, but this isn't a protocol change. It is version rolling system used by the miners. Basically they add some extra data in the first two bytes of the version number of a block.
Comments !